Demystifying HTTP and HTTPS
HTTP and HTTPS
HTTPS (Hyper Text transfer protoco secure) is basically http with security. SSL (Secure Socket Layer) certificate encrypts information users put into any website. Addtionally, HTTPS is also secured via TLS (Transport Layer Security) protocol. TLS is a succcessotr of SSL.
SSL / TLS
SSL/TLS works by binding the identities of entities such as websites and companies to cryptographic key pairs via digital documents known as X.509 certificates. Each key pair consists of a private key and a public key. The private key is kept secure, and the public key can be widely distributed via a certificate.
Glimpse on TCP , UDP and FTP
TCP provides a guarantee that document gets transferred correctly. It splits up the document into little packets and makes sure each packet gets across the network in an orderly fashion so the packets can be re-assembled into the original file. In UDP, packets can arrive in any order and some may not arrive at all. Its not suitable for transferring big/huge files.
HTTP sits on top of TCP and transfers files along with metadata. HTTP requests are sent using TCP and the server sends back it’s response (usually an HTML file) using TCP as well. It uses TCP to ensure that the entire request gets to the client or server intact.
FTP uses TCP in communication.
A poor IT Joke : I would tell you a joke about UDP …. but you might not get it 😊
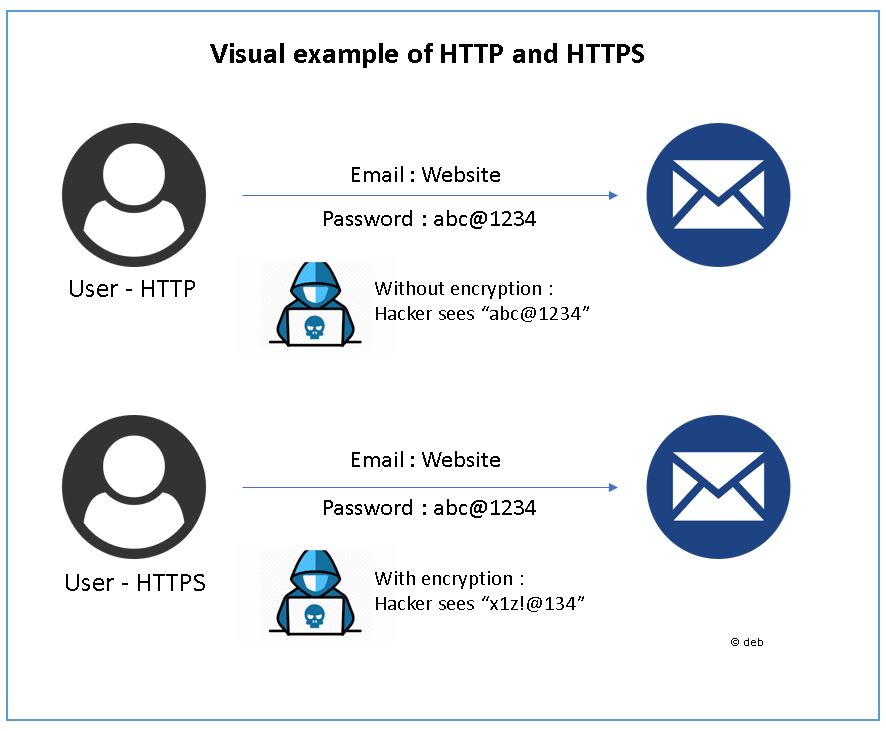
Simple example on HTTP and HTTPS
More information on SSL/TLS