Python List vs Tuple vs Dictionary
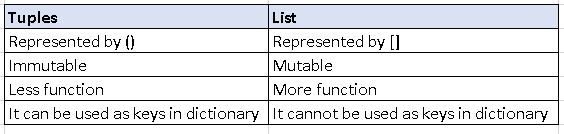
List vs Tuples
Basic functions on list
# Input list
list1= [1,2,"python","scala"]
# index 2 is included but index 3 is excluded
print("List - " ,list1[1:3])
>> List - [2, 'python']
# Index from backwards
print("List - " ,list1[-1])
>> List - scala
# Multiply on string = string
print("List - " ,list1[2]*4)
>> List - pythonpythonpythonpython
# Check data in list
print("psython" in list1)
>> False
# iterate list
for x in list1:
print(x)
>>1
2
python
scala
# length of list
print("Length of list :" , len(list2))
>> Length of list : 4
More functions can be learned from Tutorial point link
Dictionary
- Important data type in Python
- Key:Value pair , Values are mutable but Keys are immutable (string , number , tuple)
- Represented by {}
Basic functions on Dictionary
# Creating an empty Dictionary
Dict = {}
# Creating a Dictionary
# with dict() method
Dict = dict({1: 'Debaditya', 2: 'Ronaldo'})
print("\nDictionary with the use of dict(): ")
print(Dict)
# with each item as a Pair
Dict = dict([(1, 'Debaditya'), (2, 'Ronaldo')])
print("\nDictionary with each item as a pair: ")
print(Dict)
# find value from Dictionary
dictionary = {'Debaditya': 16, 'Ronaldo': 19}
search_value = 16
for name, value in dictionary.items():
if age == search_value:
print(name)
# find key from Dictionary
test_dict = {'Debaditya' : 1, 'Messi' : 2}
search_key = 'Messi'
# Using list() + keys() + index()
result = list(test_dict.keys()).index(search_key)
print(str(result))
Credits to Tutoral point - More dictionary commands are here
A few example
# Problem Statement 1
# Input : {“Gfg” : [4, 7, 5], “Best” : [8, 6, 7], “is” : [9, 3, 8]}, K = 2
# Output : [5, 7, 8]
# Explanation : The 2nd index elements are 5, 7 and 8 respectively in different keys.
list1 = []
ip = {"Gfg" : [4, 7, 5], "Best" : [8, 6, 7], "is" : [9, 3, 8]}
for name,value in ip.items():
list1.append(value[2])
print("List - ",list1)
# Counter command is used to get frequency of values in dictionary
# Merge 2 dictionary
def Merge(dict1, dict2):
res = {**dict1, **dict2}
return res
# Driver code
dict1 = {'a': 1, 'b': 2}
dict2 = {'d': 3, 'c': 4}
dict3 = Merge(dict1, dict2)
print(dict3)
>> {'b': 2, 'a': 1, 'c': 4, 'd': 3}
Notes
- Python 2.7 : int and long int
- Python 3 there is only one type : int