Trees in ML World
Trees are well-known as a non-linear data structure. They don’t store data in a linear way. They organize data hierarchically.
A tree is a collection of entities called nodes. Nodes are connected by edges. Each node contains a value or data, and it may or may not have a child node.
The Image at the beginning of the article (Source) explains the terminologies of a Tree.
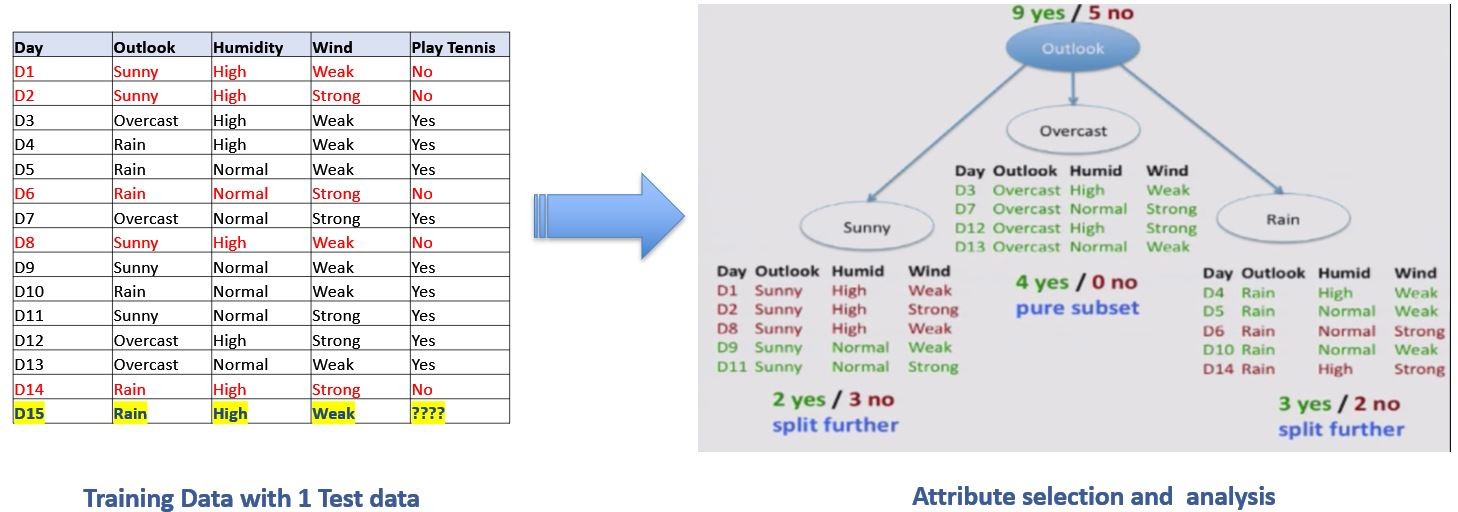
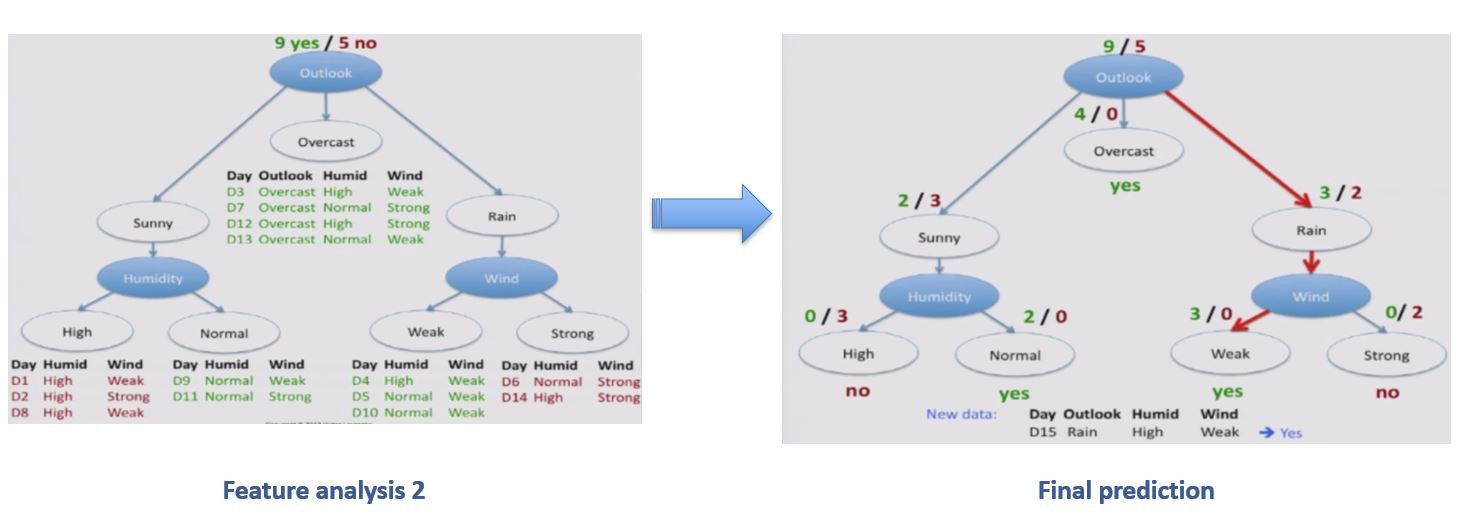
Decision Trees
Decision trees represent rules, which can be understood by humans and used in knowledge system such as database
Strengths
- Less computation process is required
- Rules generated by Decision trees are quite easy to understand
Weakness
- Perform poorly with many class and small data.
- Training is computationally expensive process . As at each node, each field (which is getting splitted) must be sorted before its best split can be found.
- Its not the best choice for predicting continuous attributes
- Random Forrest
- Learning ensemble consisting of a bagging of un-pruned decision tree learners with a randomized selection of features at each split
Purpose (in nutshell)
- Definition : Collection of unpruned CARTs + Rule to combine individual tree decisions
- Purpose : Improve prediction accuracy
- Principle : Encouraging diversity among the tree
- Solution : Bagging + Random decision trees (rCART)
Random Forrest
Flow
- Let N trees be the number of trees to build for each of N trees iterations
- Select a new bootstrap sample (See Bagging) from training set
- Grow an un-pruned tree on this bootstrap.
- At each internal node, randomly select ‘m’ predictors and determine the best split using only these predictors.
- Do not perform cost complexity pruning. Save tree as is, along side those built thus far.
- Output overall prediction as the average response (regression) or majority vote (classification) from all individually trained trees
Strengths
- Unlike decision trees - it can handle thousands of input variables without variable deletion.
- Forrest generated during the process can be used for other tasks
- With my personal experience , it runs efficiently on large datasets
Weakness
- It has been observed to overfit for some datasets with noisy classification/regression tasks.
- The categorical variables with different number of levels, the algorithm is biased in favor of those attributes with more levels.
My DataBricks Notebook
I am publishing my Databricks Notebook where I have tested the Decision Tree and Random Forrest Spark code (which is referred from Apache Spark site)
Decision Trees
import org.apache.spark.ml.Pipeline
import org.apache.spark.ml.classification.DecisionTreeClassificationModel
import org.apache.spark.ml.classification.DecisionTreeClassifier
import org.apache.spark.ml.evaluation.MulticlassClassificationEvaluator
import org.apache.spark.ml.feature.{IndexToString, StringIndexer, VectorIndexer}
// Load the data stored in LIBSVM format as a DataFrame.
val data = spark.read.format("libsvm").load("/FileStore/tables/libsvm.txt")
// Index labels, adding metadata to the label column.
// Fit on whole dataset to include all labels in index.
val labelIndexer = new StringIndexer()
.setInputCol("label")
.setOutputCol("indexedLabel")
.fit(data)
// Automatically identify categorical features, and index them.
val featureIndexer = new VectorIndexer()
.setInputCol("features")
.setOutputCol("indexedFeatures")
.setMaxCategories(4) // features with > 4 distinct values are treated as continuous.
.fit(data)
// Split the data into training and test sets (30% held out for testing).
val Array(trainingData, testData) = data.randomSplit(Array(0.7, 0.3))
// Train a DecisionTree model.
val dt = new DecisionTreeClassifier()
.setLabelCol("indexedLabel")
.setFeaturesCol("indexedFeatures")
// Convert indexed labels back to original labels.
val labelConverter = new IndexToString()
.setInputCol("prediction")
.setOutputCol("predictedLabel")
.setLabels(labelIndexer.labels)
// Chain indexers and tree in a Pipeline.
val pipeline = new Pipeline()
.setStages(Array(labelIndexer, featureIndexer, dt, labelConverter))
// Train model. This also runs the indexers.
val model = pipeline.fit(trainingData)
// Make predictions.
val predictions = model.transform(testData)
// Select example rows to display.
predictions.select("predictedLabel", "label", "features").show(5)
// Select (prediction, true label) and compute test error.
val evaluator = new MulticlassClassificationEvaluator()
.setLabelCol("indexedLabel")
.setPredictionCol("prediction")
.setMetricName("accuracy")
val accuracy = evaluator.evaluate(predictions)
println(s"Test Error = ${(1.0 - accuracy)}")
val treeModel = model.stages(2).asInstanceOf[DecisionTreeClassificationModel]
println(s"Learned classification tree model:\n ${treeModel.toDebugString}")
Link for Databricks - Decision Trees
Random Forrest
import org.apache.spark.ml.Pipeline
import org.apache.spark.ml.classification.{RandomForestClassificationModel, RandomForestClassifier}
import org.apache.spark.ml.evaluation.MulticlassClassificationEvaluator
import org.apache.spark.ml.feature.{IndexToString, StringIndexer, VectorIndexer}
// Load and parse the data file.
val data = spark.read.format("libsvm").load("/FileStore/tables/libsvm.txt")
// Index labels, adding metadata to the label column.
// Fit on whole dataset to include all labels in index.
val labelIndexer = new StringIndexer()
.setInputCol("label")
.setOutputCol("indexedLabel")
.fit(data)
// Automatically identify categorical features, and index them.
// Set maxCategories so features with > 4 distinct values are treated as continuous.
val featureIndexer = new VectorIndexer()
.setInputCol("features")
.setOutputCol("indexedFeatures")
.setMaxCategories(4)
.fit(data)
// Split the data into training and test sets (30% held out for testing).
val Array(trainingData, testData) = data.randomSplit(Array(0.8, 0.2))
// Train a RandomForest model.
val rf = new RandomForestClassifier()
.setLabelCol("indexedLabel")
.setFeaturesCol("indexedFeatures")
.setNumTrees(10)
// Convert indexed labels back to original labels.
val labelConverter = new IndexToString()
.setInputCol("prediction")
.setOutputCol("predictedLabel")
.setLabels(labelIndexer.labels)
// Chain indexers and forest in a Pipeline.
val pipeline = new Pipeline()
.setStages(Array(labelIndexer, featureIndexer, rf, labelConverter))
// Train model. This also runs the indexers.
val model = pipeline.fit(trainingData)
// Make predictions.
val predictions = model.transform(testData)
// Select example rows to display.
predictions.select("predictedLabel", "label", "features").show(5)
// Select (prediction, true label) and compute test error.
val evaluator = new MulticlassClassificationEvaluator()
.setLabelCol("indexedLabel")
.setPredictionCol("prediction")
.setMetricName("accuracy")
val accuracy = evaluator.evaluate(predictions)
println(s"Test Error = ${(1.0 - accuracy)}")
val rfModel = model.stages(2).asInstanceOf[RandomForestClassificationModel]
println(s"Learned classification forest model:\n ${rfModel.toDebugString}")
Link for Databricks - Random forrest
Note
This article is prepared after reading a lot of articles from various sources (blogs,pdfs,lectures,videos,etc) and articulating them in single blog.
For this article, we will keep it short with Decision and Random Forrest - Next article will be followed with Gradient Boost (with more details) and the famous XGBOOST.
Sources
- https://www.cse.ust.hk/~twinsen/Decision_Tree.ppt
- https://www.stat.berkeley.edu/~breiman/RandomForests/cc_home.htm
- http://www.cs.ucsb.edu/~ambuj/Courses/165B/Lectures/ensemble%20learning.ppt
- https://www.edureka.co/community/46102/disadvantages-of-using-decision-tree
- https://perso.math.univ-toulouse.fr/motimo/files/2013/07/random-forest.pdf
- https://www.datasciencecentral.com/profiles/blogs/decision-tree-vs-random-forest-vs-boosted-trees-explained
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eKD5gxPPeY0
- https://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/ml-classification-regression.html